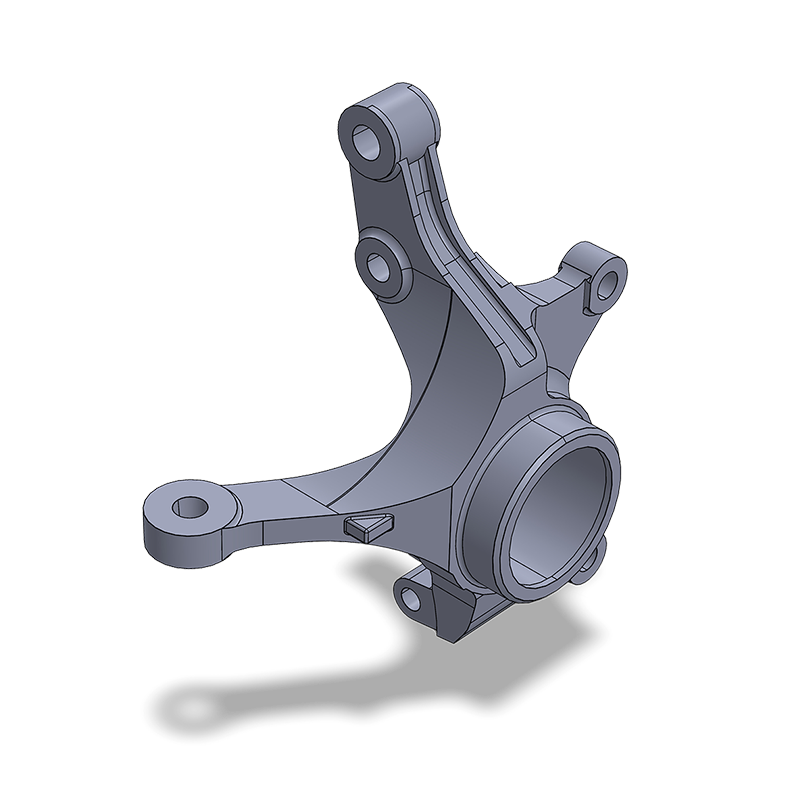




Castings engineering focuses on the design of casting and forged components for the manufacturing industry. The process stands out due to its extensive design freedom and the ability to integrate complex geometries, weight reduction, and functionality directly into a single part. Musd Engineering combines in-depth expertise in materials, process selection, and design principles to deliver reliable, scalable, and cost-effective solutions.
The success of a casting starts with design optimization: smooth transitions, uniform wall thicknesses, and integrated functions. This often allows welded assemblies or machined parts to be replaced by a single casting, reducing production steps and lowering failure risk.
Process, Material Selection, and Finishing.
Investment casting, sand casting, or forging. Common materials include:
Depending on requirements, secondary processes such as CNC machining, heat treatment, or surface coatings ensure dimensional accuracy and durability.
While tooling requires an initial investment, cost per part decreases significantly in medium to large series. Quality is guaranteed through casting simulation software and non-destructive testing (X-ray, ultrasonic). Innovations such as 3D-printed molds, automation, and AI shorten lead times and increase reliability.
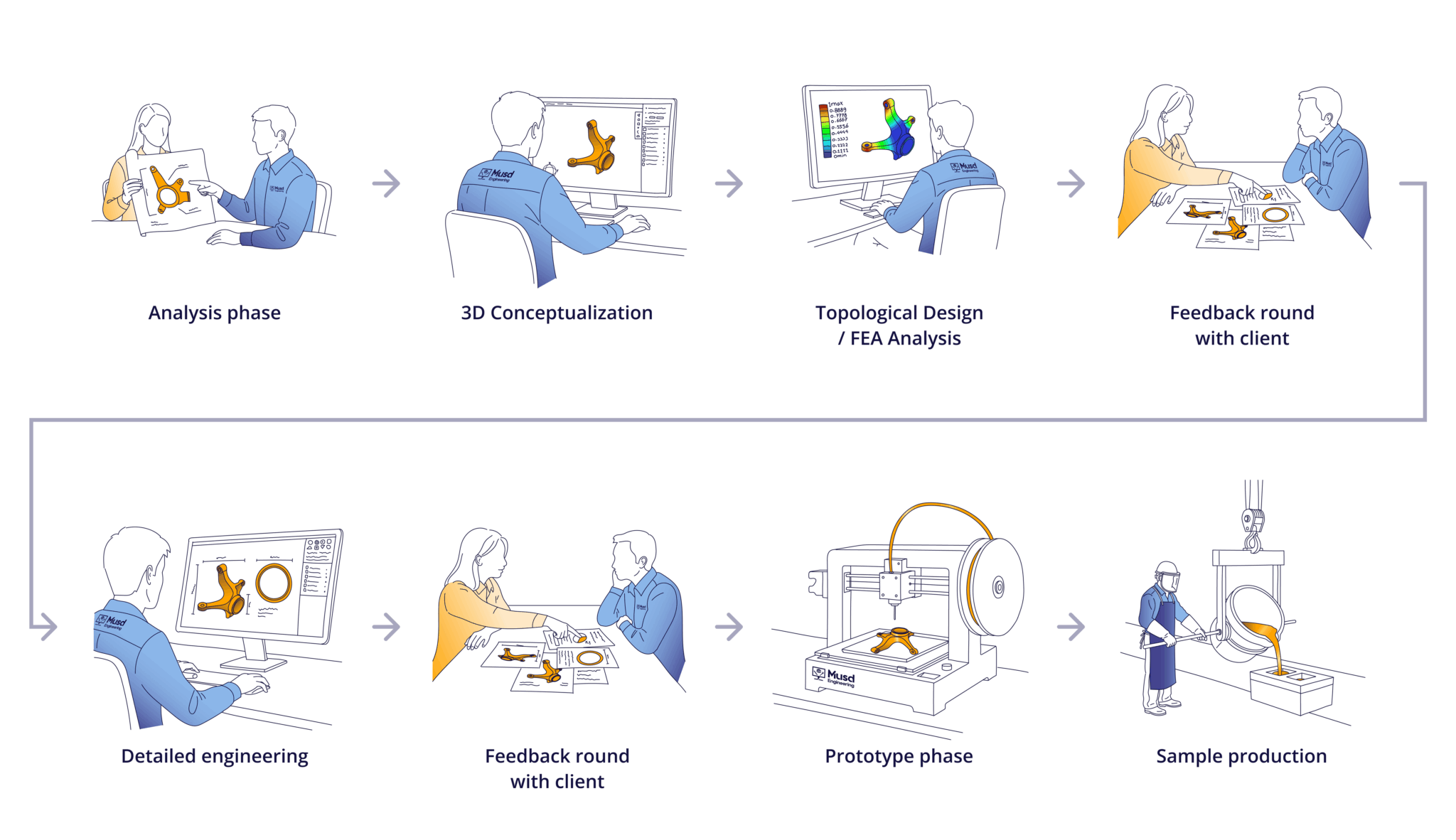
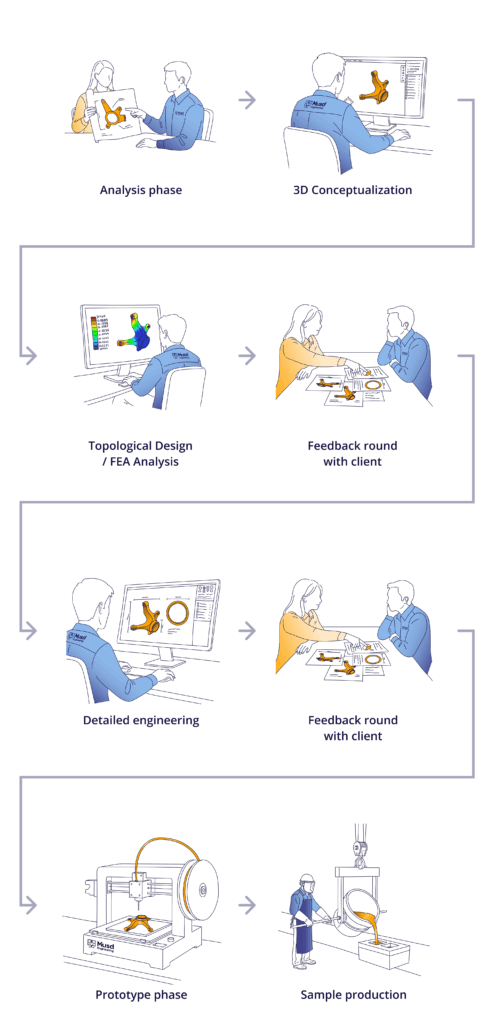
For projects involving the design of cast and forged parts, we use the following approach.